
- #Which are used to create a raster image how to#
- #Which are used to create a raster image zip file#
- #Which are used to create a raster image software#
- #Which are used to create a raster image license#
- #Which are used to create a raster image series#
To make sure that the classes represented by the training samples are distinguishable, their spectral characteristics need to be checked. You will use this in supervised classification at later stage. Once you are done collecting training samples, click the Create Signature File icon on the Training Sample Manager to save the signature file to your local hard disk. The classes that were created using training samples We repeated this process for the additional classes shown in Figure 5.įigure 5. In our example, we first collected samples for forest and named the class “Forest” and chose a dark green to represent the class. Provide a relevant class name and select a color to represent the class. Then use the Merge tool to merge the samples for each class. The same process would be repeated for the other land cover classes you want to create (C).Ĭollect a few training samples for each of the classes you want to classify. Each sample shows up as a separate class (B) but I want them all to be forest so I have to use the Merge function to make them one class, to call it forest and to assign it a color of green. In my example, I took 5 samples that I thought represented forest (A). Refer to this ArcGIS online help topic, Creating training samples to follow the step-by-step instructions for collecting the training samples.įigure 4. Using the Training sample drawing tools (figure 1), you can collect the training samples for your area of interest.Īdding the area of interest (AOI) polygon to ArcMap helps you focus on the area within the image that you want to classify. This is the mechanism for managing training samples to edit the class names or values, merge and split classes, delete classes, change display colors, load and save training samples, evaluate training samples, and create signature files. When you click this, it opens the Training Sample Manager (figure 3). On this toolbar, to the right of the Layer drop down box is the Training Sample Manager icon. It also serves as a central location for performing both supervised classification and unsupervised classification using ArcGIS Spatial Analyst.įigure 2.
#Which are used to create a raster image series#
A signature file records the spectral signatures of different classes across a series of bands) for supervised classification. The Image Classification toolbar provides a user-friendly environment for creating training samples and signature files.
#Which are used to create a raster image license#
Bands 4, 3, and 2 are displayed rendering a color infrared imageĪfter enabling the Spatial Analyst extension, you can add the Image Classification toolbar to your ArcMap interface (you will need a Spatial Analyst license to use the toolbar). The LandsatGLSTM_Multispectral_2000 image. This is the extent that is shown in ArcMap when you open the. So we added an AOI polygon feature class to the Table of Contents and zoomed into the area that we want to map. The image service contains data for whole world and in this case we want to focus on small area of interest.
To start, open the Landsat_SupervisedClassification.mxd in the zip file, which has TM_Multispectral_2000 image service (4, 3, 2 band combination) and an area of interest (AOI) polygon already added to the Table of Contents.

#Which are used to create a raster image zip file#
If you want to follow along, you can download the zip file we created for you to try this out yourself.
#Which are used to create a raster image how to#
In this blog entry, we explain how to use the Landsat image services with supervised classification method to create a land cover map. Once the clusters are found, you then need to identify what the cluster represents (e.g., water, bare earth, dry soil, etc…)
#Which are used to create a raster image software#
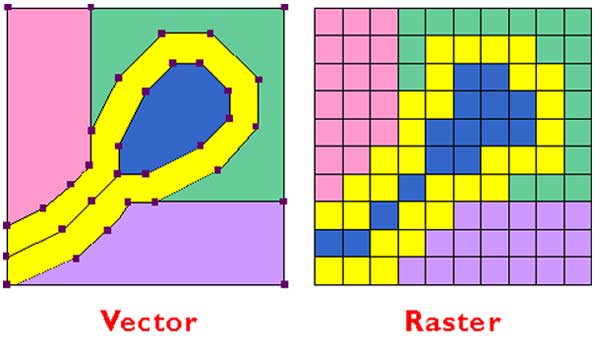
With the unsupervised classification method, the software finds the spectral classes (or clusters) in the multi-band image without the analyst’s intervention, thus being unsupervised. These samples are collected by you, the image analyst, to classify the image. Using the supervised classification method, an image is classified using spectral signatures (i.e., reflectance values) obtained from training samples (polygons that represent distinct sample areas of the different land cover types to be classified). There are two primary ways to classify a multi-band raster image supervised and unsupervised classification. The image classification process involves conversion of multi-band raster imagery into a single-band raster with a number of categorical classes that relate to different types of land cover. In this blog entry, we dive further into Landsat image services and describe how you can create thematic land cover maps which can then be used for analyses, such as land cover change detection. In a previous blog entry, we discussed how you can use Landsat image services in ArcMap to see the change over time. By Rajinder Nagi, Esri Cartographic Product Engineer


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
